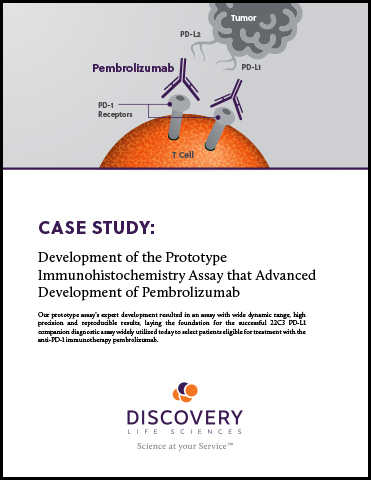
Our prototype assay’s expert development resulted in an assay with wide dynamic range, high precision and reproducible results, laying the foundation for the successful 22C3 PD-L1 companion diagnostic assay widely utilized today to select patients eligible for treatment with the anti-PD-1 immunotherapy pembrolizumab.
Scope
The ability to reliably and simply measure PD-L1 expression in tumor tissue may identify subsets of patients who might achieve better outcomes with anti–PD-1 or anti–PD-L1 therapeutics. QualTek experts (now part of Discovery Life Sciences) collaborated with experts from Merck Research Laboratories to develop a prototype immunohistochemistry (IHC) assay for measuring PD-L1 expression among patients enrolled in Merck-sponsored clinical trials to predict those who have a higher likelihood of responding to Merck’s immune checkpoint inhibitor, pembrolizumab.
Background
The programmed death receptor-1 (PD-1) pathway is one of the major immune-checkpoints that engages with tumor cells to avoid T-cell–mediated immune surveillance. The PD-1 receptor-1 ligand (PD-L1), which is often expressed by tumor cells, binds with PD-1 on T cells and delivers an inhibitor signal to down-regulate T cell proliferation and activation – enabling tumor expansion and growth.
Given its role in tumor progression, the PD-1 pathway is a common target for immunotherapies. The first clinical trial of a PD-L1-blocking drug began in 2006 in patients with a variety of tumors including melanoma, kidney, and lung. Today, six PD-1/L1 checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapies have been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration for 14 different types of cancer, and PD-1/L1 inhibitors are being evaluated in more than 2,250 clinical trials.
